LeetCode - Path Sum III
Problem statement
Given the root of a binary tree and an integer targetSum, return the number of paths where the sum of the values along the path equals targetSum.
The path does not need to start or end at the root or a leaf, but it must go downwards (i.e., traveling only from parent nodes to child nodes).
Problem statement taken from: https://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum-iii
Example 1:
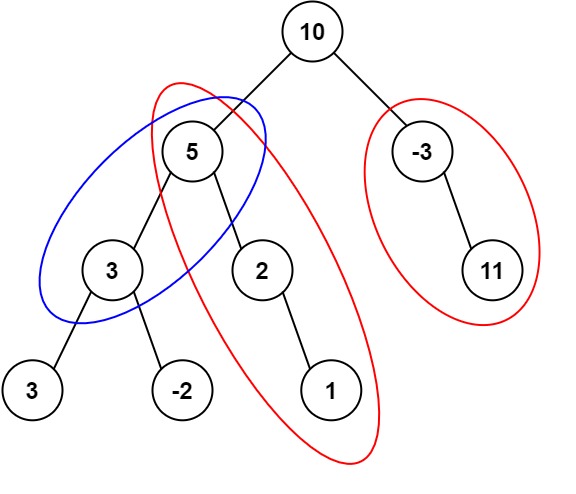
Input: root = [10, 5, -3, 3, 2, null, 11, 3, -2, null, 1], targetSum = 8
Output: 3
Explanation: The paths that sum to 8 are shown.
Example 2:
Input: root = [5, 4, 8, 11, null, 13, 4, 7, 2, null, null, 5, 1], targetSum = 22
Output: 3
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 1000].
- -10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9
- -1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
Explanation
Recursion
The problem is similar to our previous blog posts Path Sum and Path Sum II.
We need to change the algorithm a bit to count the different paths in the tree. We will use the DFS algorithm to count the paths. Let's check the algorithm.
// pathSum method
- if root == null
- return 0
- return dfs(root, 0, targetSum) +
pathSum(root->left, targetSum) +
pathSum(root->right, targetSum)
// dfs method
- if root == null
- return 0
- set currentSum = previousSum + root->val
count = 0
- if currentSum == targetSum
- count = 1
- return count +
dfs(root->left, currentSum, targetSum) +
dfs(root->right, currentSum, targetSum)
The time-complexity can be reduced to O(nlog(n)) by reversing the linked list.
Let's check our algorithm in C++, Golang, and Javascript.
C++ solution
class Solution {
public:
int dfs(TreeNode* root, long long previousSum, long long targetSum) {
if(root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int currentSum = previousSum + root->val;
int count = 0;
if(currentSum == targetSum) {
count = 1;
}
return count + dfs(root->left, currentSum, targetSum) + dfs(root->right, currentSum, targetSum);
}
int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if(root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
return dfs(root, 0, targetSum) + pathSum(root->left, targetSum) + pathSum(root->right, targetSum);
}
};Golang solution
func dfs(root *TreeNode, previousSum, targetSum int) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
currentSum := previousSum + root.Val
count := 0
if currentSum == targetSum {
count = 1
}
return count + dfs(root.Left, currentSum, targetSum) + dfs(root.Right, currentSum, targetSum)
}
func pathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
return dfs(root, 0, targetSum) + pathSum(root.Left, targetSum) + pathSum(root.Right, targetSum)
}Javascript solution
var dfs = function(root, previousSum, targetSum) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
let currentSum = previousSum + root.val;
let count = 0;
if(currentSum == targetSum) {
count = 1;
}
return count + dfs(root.left, currentSum, targetSum) + dfs(root.right, currentSum, targetSum);
};
var pathSum = function(root, targetSum) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
return dfs(root, 0, targetSum) + pathSum(root.left, targetSum) + pathSum(root.right, targetSum);
};Dry Run
Let's dry-run our algorithm to see how the solution works.
Input: root = [10, 5, -3, 3, 2, null, 11, 3, -2, null, 1]
targetSum = 8
// pathSum method
Step 1: if root == NULL
root -> 10
false
Step 2: dfs(root, 0, targetSum) + pathSum(root->left, targetSum) + pathSum(root->right, targetSum)
dfs(->10, 0, 8) + pathSum(->5, 8) + pathSum(-3, 8)
// dfs method
Step 3: if root == NULL
root -> 10
false
currentSum = previousSum + root->val
= 0 + 10
= 10
count = 0
currentSum == targetSum
10 == 8
false
count + dfs(root->left, currentSum, targetSum) + dfs(root->right, currentSum, targetSum)
0 + dfs(->5, 10, 8) + dfs(->(-3), 10, 8)
// dfs(->5, 10, 8)
Step 4: if root == NULL
root -> 5
false
currentSum = previousSum + root->val
= 10 + 5
= 15
count = 0
currentSum == targetSum
15 == 8
false
count + dfs(root->left, currentSum, targetSum) + dfs(root->right, currentSum, targetSum)
0 + dfs(->3, 15, 8) + dfs(2, 15, 8)
// dfs(->3, 15, 8)
Step 5: if root == NULL
root -> 3
false
currentSum = previousSum + root->val
= 15 + 3
= 18
count = 0
currentSum == targetSum
18 == 8
false
count + dfs(root->left, currentSum, targetSum) + dfs(root->right, currentSum, targetSum)
0 + dfs(->3, 18, 8) + dfs(->(-2), 18, 8)
// dfs(->3, 18, 8)
Step 6: if root == NULL
root -> 3
false
currentSum = previousSum + root->val
= 18 + 3
= 21
count = 0
currentSum == targetSum
21 == 8
false
count + dfs(root->left, currentSum, targetSum) + dfs(root->right, currentSum, targetSum)
0 + dfs(->nil, 21, 8) + dfs(->nil, 21, 8)
Both dfs(->nil, 21, 8), dfs(->nil, 21, 8) node is nil so we return 0 and backtrack to Step 5
0 + dfs(->3, 18, 8) + dfs(->(-2), 18, 8) where we solve for
dfs(->(-2), 18, 8)
// dfs(->(-2), 18, 8)
Step 7: if root == NULL
root -> -2
false
currentSum = previousSum + root->val
= 21 + -2
= 19
count = 0
currentSum == targetSum
19 == 8
false
count + dfs(root->left, currentSum, targetSum) + dfs(root->right, currentSum, targetSum)
0 + dfs(->nil, 19, 8) + dfs(->nil, 19, 8)
Both dfs(->nil, 19, 8), dfs(->nil, 19, 8) node is nil so we return 0 and backtrack to Step 4
0 + dfs(->3, 15, 8) + dfs(2, 15, 8) where we solve for
dfs(2, 15, 8)
// dfs(2, 15, 8)
Step 8: if root == NULL
root -> 2
false
currentSum = previousSum + root->val
= 15 + 2
= 17
count = 0
currentSum == targetSum
17 == 8
false
count + dfs(root->left, currentSum, targetSum) + dfs(root->right, currentSum, targetSum)
0 + dfs(->nil, 17, 8) + dfs(1, 17, 8)
dfs(->nil, 17, 8) returns 0 as node is nil, so we evaluate for
dfs(1, 17, 8)
// dfs(1, 17, 8)
Step 9: if root == NULL
root -> 1
false
currentSum = previousSum + root->val
= 17 + 1
= 18
count = 0
currentSum == targetSum
18 == 8
false
count + dfs(root->left, currentSum, targetSum) + dfs(root->right, currentSum, targetSum)
0 + dfs(->nil, 18, 8) + dfs(->nil, 18, 8)
Both dfs(->nil, 19, 8), dfs(->nil, 19, 8) node is nil so we return 0 and backtrack to Step 3
0 + dfs(->5, 10, 8) + dfs(->(-3), 10, 8) where we solve for
dfs(->(-3), 10, 8)
// dfs(->(-3), 10, 8)
Step 10: if root == NULL
root -> -3
false
currentSum = previousSum + root->val
= 10 + -3
= 7
count = 0
currentSum == targetSum
7 == 8
false
count + dfs(root->left, currentSum, targetSum) + dfs(root->right, currentSum, targetSum)
0 + dfs(->nil, 7, 8) + dfs(->11, 7, 8)
dfs(->nil, 7, 8) returns 0 as node is nil, so we evaluate for
dfs(->11, 7, 8)
// dfs(->11, 7, 8)
Step 11: if root == NULL
root -> 11
false
currentSum = previousSum + root->val
= 7 + 11
= 18
count = 0
currentSum == targetSum
18 == 8
false
count + dfs(root->left, currentSum, targetSum) + dfs(root->right, currentSum, targetSum)
0 + dfs(->nil, 18, 8) + dfs(->nil, 18, 8)
Both dfs(->nil, 18, 8), dfs(->nil, 18, 8) node is nil so we return 0 and backtrack to Step 2
dfs(->10, 0, 8) + pathSum(->5, 8) + pathSum(-3, 8)
where we have dfs(->10, 0, 8) as 0
and we evaluate for pathSum(->5, 8)
// pathSum(->5, 8)
Step 12: if root == NULL
root -> 5
false
dfs(root, 0, targetSum) + pathSum(root->left, targetSum) + pathSum(root->right, targetSum)
dfs(->5, 0, 8) + pathSum(->3, 8) + pathSum(->2, 8)
// dfs(->5, 0, 8)
Step 13: if root == NULL
root -> 5
false
currentSum = previousSum + root->val
= 0 + 5
= 5
count = 0
currentSum == targetSum
5 == 8
false
count + dfs(root->left, currentSum, targetSum) + dfs(root->right, currentSum, targetSum)
0 + dfs(->3, 5, 8) + dfs(->2, 5, 8)
// dfs(->3, 5, 8)
Step 14: if root == NULL
root -> 3
false
currentSum = previousSum + root->val
= 5 + 3
= 8
count = 0
currentSum == targetSum
8 == 8
true
count = 1
count + dfs(root->left, currentSum, targetSum) + dfs(root->right, currentSum, targetSum)
1 + dfs(->3, 8, 8) + dfs(->(-2), 8, 8)
We similarly iterate over the rest of the tree and return the count.