LeetCode - Symmetric tree
Problem statement
Given the root of a binary tree, check whether it is a mirror of itself (i.e., symmetric around its center).
Problem statement taken from: https://leetcode.com/problems/symmetric-tree
Example 1:
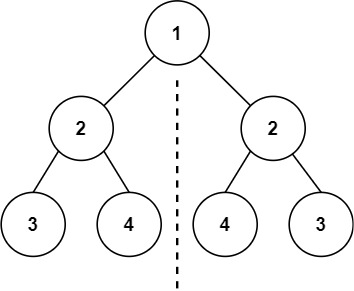
Input: root = [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 3]
Output: true
Example 2:
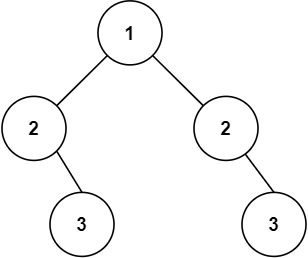
Input: root = [1, 2, 2, null, 3, null, 3]
Output: false
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 1000].
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Explanation
Recursive function
When it comes to solving problems related to trees, recursion is the best choice. If not recursion, the iterative approach will use queues.
Let's explore a simple recursive approach in this blog. The approach is to use two pointers as arguments that points to the root of the tree. The first pointer will move left and second will move right and verify if the nodes are same or not.
Let's check the algorithm.
// main function
- call recursive function areSymmetric(root, root)
// areSymmetric function(root1, root2)
- if !root1 && !root2
- return true
- else
- if root1 && root2
- if root1->val == root2->val
- return areSymmetric(root1->left, root2->right) && areSymmetric(root1->right, root2->left)
- return false
C++ solution
bool areSymmetric(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2){
if(!root1 && !root2){
return true;
} else {
if(root1 && root2){
if(root1->val == root2->val){
return areSymmetric(root1->left, root2->right) &&
areSymmetric(root1->right, root2->left);
}
}
return false;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
return areSymmetric(root, root);
}
};Golang solution
func areSymmetric(root1 *TreeNode, root2 *TreeNode) bool {
if root1 == nil && root2 == nil {
return true
} else {
if root1 != nil && root2 != nil {
if root1.Val == root2.Val {
return areSymmetric(root1.Left, root2.Right) && areSymmetric(root1.Right, root2.Left)
}
}
}
return false
}
func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool {
return areSymmetric(root, root)
}Javascript solution
var areSymmetric = function(root1, root2) {
if(!root1 && !root2) {
return true;
} else {
if(root1 && root2) {
if(root1.val == root2.val) {
return areSymmetric(root1.left, root2.right) && areSymmetric(root1.right, root2.left);
}
}
}
return false;
}
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
return areSymmetric(root, root);
};Dry Run
Let's dry-run our algorithm to see how the solution works.
Input: root = [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 3]
// in main function
Step 1: return areSymmetric(root, root)
// in areSymmetric function
Step 2: if !root1 && !root2
- root1 != nil
1 != nil
true
- root2 != nil
1 != nil
true
- !true && !true
- false
else
if root1 && root2
- 1 && 1
- true
if root1->val == root2->val
- 1 == 1
- true
return areSymmetric(root1->left, root2->right) && areSymmetric(root1->right && root2->left)
return areSymmetric(2, 2) && areSymmetric(2, 2)
// we will ignore the 2nd condition here, since both are same.
// In actual recursive call it will be evaluated.
Step 3: if !root1 && !root2
- root1 != nil
2 != nil
true
- root2 != nil
2 != nil
true
- !true && !true
- false
else
if root1 && root2
- 2 && 2
- true
if root1->val == root2->val
- 2 == 2
- true
return areSymmetric(root1->left, root2->right) && areSymmetric(root1->right && root2->left)
return areSymmetric(3, 3) && areSymmetric(4, 4)
// areSymmetric(3, 3)
Step 4: if !root1 && !root2
- root1 != nil
3 != nil
true
- root2 != nil
3 != nil
true
- !true && !true
- false
else
if root1 && root2
- 3 && 3
- true
if root1->val == root2->val
- 3 == 3
- true
return areSymmetric(root1->left, root2->right) && areSymmetric(root1->right && root2->left)
return areSymmetric(nil, nil) && areSymmetric(nil, nil)
// areSymmetric(nil, nil)
Step 5: if !root1 && !root2
- root1 != nil
nil != nil
false
- root2 != nil
nil != nil
false
- !false && !false
- true
// areSymmetric(4, 4)
Step 6: if !root1 && !root2
- root1 != nil
4 != nil
true
- root2 != nil
4 != nil
true
- !true && !true
- false
else
if root1 && root2
- 4 && 4
- true
if root1->val == root2->val
- 4 == 4
- true
return areSymmetric(root1->left, root2->right) && areSymmetric(root1->right && root2->left)
return areSymmetric(nil, nil) && areSymmetric(nil, nil)
// areSymmetric(nil, nil) returns true
// so we move back from step 6 to step 5 till step 2 and evaluate
return areSymmetric(root1->left, root2->right) && areSymmetric(root1->right && root2->left)
// which is true
So the answer we return is true.